The Impact of Rapid Application Development and Why is it Important?
Mar 10, 2023
Rapid Application Development is a software development process that helps companies with little or no experience in software development build applications quickly. This approach involves taking advantage of tools, techniques and methodologies that have been proven effective at building high-quality mobile and web apps more quickly than traditional methods.
The advantages of Rapid Application Development are:
- It's faster than traditional application development techniques because it doesn't require extensive planning or design work before coding begins.
- Code reuse is easier because developers don't have to write new code from scratch for each new project as they do with other methods.
What is Rapid Application Development?
RAD (Rapid Application Development) is a software development methodology that emphasizes iterative, rapid prototyping and development of software applications. The goal of RAD is to reduce the time it takes to develop a software application, while still ensuring high quality and meeting customer requirements.
RAD development involves a collaborative approach to software development, with close communication between developers and end-users. It typically involves the use of visual modeling tools and code generators, which allow developers to quickly build working prototypes of software applications. These prototypes can then be refined and improved through iterative cycles of feedback and development.
Rapid application development can be used for a variety of purposes, but it’s most commonly associated with the creation of web apps that need to be built quickly or at a low cost. The term “rapid” implies that these types of projects aren’t meant to last long—they should have an end date when they are complete and ready for deployment into production environments.
RAD programming is particularly well-suited to projects with rapidly changing requirements, as it allows developers to quickly adapt to changing customer needs and respond to feedback. However, it may not be suitable for all types of projects, particularly those that require a high degree of reliability, security, or scalability.
The idea behind rapid application development is simple: create something quickly, test it out, make improvements as needed, and then move on to another project until your next deadline rolls around again!
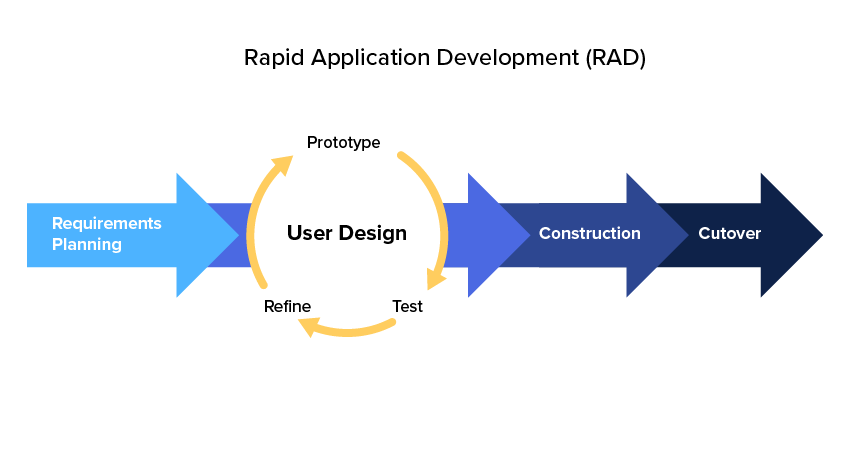
The 4 steps of Rapid Application Development
RAD typically involves four main steps, which are as follows:
1. Requirements Planning: In this initial stage, the software development team works closely with the end users to identify and define the requirements of the software application. This typically involves gathering feedback and input from stakeholders, identifying any potential challenges or constraints, and creating a project plan.
2. User Design: Once the requirements have been identified, the development team works on creating a basic user interface for the application. This may involve creating mockups or prototypes of the user interface, which can be used to gather further feedback and input from end users. This stage typically involves a high level of collaboration and communication between the development team and the end users.
3. Construction: During the construction stage, the development team builds the actual software application. This is typically done in short, iterative cycles, with each cycle focusing on a specific set of features or functionality. The use of code generators and other automated tools can help speed up the development process, allowing the team to quickly build and test the application.
4. Cutover: Once the application has been built and tested, it is deployed to the end users. This may involve a gradual rollout, with the application being tested and refined in a real-world environment. The development team may also provide training and support to end-users during this stage, helping to ensure a smooth transition to the new software application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RAD
RAD (Rapid Application Development) has several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when evaluating it as a software development methodology.
Advantages:
1. Faster Development: One of the key advantages of RAD is that it allows for faster development of software applications. By using iterative development cycles, RAD enables development teams to rapidly prototype and test software, and make changes quickly based on feedback. This can be useful for companies that need to quickly develop and deploy software solutions to meet their business needs or even to stay ahead of their competition.
2. Increased Collaboration: RAD typically involves close collaboration between developers and end-users, which can help to ensure that the final software application meets the needs of the organization. By involving end-users early in the development process, RAD can help to identify potential issues or challenges early on, allowing the development team to address them before they become major problems.
3. Reduced Costs: By streamlining the development process and reducing the amount of time required to build and test software applications, rapid software development can help to reduce development costs. This can be particularly valuable for organizations with limited budgets or tight timelines.
Disadvantages:
1. Limited Scalability: One of the main disadvantages of RAD is that it may not be well-suited for large or complex software projects. Because RAD relies heavily on iterative development cycles and rapid prototyping, it may not be able to accommodate the complex architecture or scalability requirements of larger projects.
2. Potential for Incomplete Requirements: Because RAD involves a highly collaborative approach to software development, there is a risk that important requirements may be overlooked or missed. This can lead to a final software application that does not fully meet the needs of the organization.
3. Limited Reusability: RAD relies heavily on code generators and other automated tools, which may limit the reusability of the code. This can be a disadvantage for organizations that need to build multiple software applications or reuse code across different projects.
Overall, RAD can be an effective software development methodology for organizations that need to rapidly develop and deploy software applications. However, it may not be suitable for all projects, and careful consideration should be given to its advantages and disadvantages before adopting it as a development approach.
Competitive Advantage to Businesses
RAD (Rapid Application Development) can provide several competitive advantages for organizations, including the following:
1. Faster Time-to-Market: By enabling faster development of software applications, RAD can help organizations bring products to market more quickly than their competitors.
2. Increased Flexibility: RAD allows development teams to quickly adapt to changing customer requirements, which can help organizations stay ahead of the competition. By enabling rapid prototyping and iteration, RAD can help organizations respond to changing market conditions and customer needs in real-time.
3. Better Collaboration: RAD involves close collaboration between developers and end-users, which can help organizations to better understand customer needs and preferences. By involving end-users early in the development process, organizations can ensure that the final software application meets the needs of its target audience, which can provide a competitive advantage.
4. Lower Development Costs: RAD can help organizations to reduce development costs by streamlining the development process and reducing the amount of time required to build and test software applications. This can be particularly valuable for organizations with limited budgets or tight timelines.
5. Improved Quality: By enabling rapid prototyping and iteration, RAD can help organizations identify and address potential issues or defects early in the development process. This can help to ensure that the final software application is of high quality and meets customer requirements, which can provide a competitive advantage.
Overall, RAD can provide a competitive advantage for organizations by enabling faster time-to-market, increased flexibility, better collaboration, lower development costs, and improved quality. However, it may not be the best approach for all projects, and careful consideration should be given to its advantages and disadvantages before adopting it as a development approach.
Case Study
A client was looking for a way to increase the efficiency of their application development team. They had an existing workflow that involved creating many different types of applications with different versions and types of data, which made it difficult for them to keep track of what was happening or where things were at any given time.
The solution? Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Using RAD tools like Zendesk and Teamtreehouse, they were able to create a new system that allowed everyone on their team, from developers to testers, to work together in real-time on projects as they progressed through development stages. This created more transparency between teams, allowing them all access at once rather than having multiple people working independently on separate parts at once (which isn't always ideal).
In Conclusion
With all the advantages and disadvantages of RAD, it's important to know what your goals are before you start. If you're just looking for something easy and quick, then this may be an option for you. If however, like many others who have decided to give RAD a try, you want more than just an easy project at hand, then go ahead and think about what other benefits might come with such a process.
Read more: 6 Best Zapier Alternatives: Automate your Business Today!
Blogs & Insights
We'd love to share our knowledge with you. Get updates through our blogs & know what’s going on in the no-code world.